PCI DSS Compliance
See how PayU supports PCI compliance while ensuring smooth and secure transactions.
Learn moreIn a tokenized transaction, sensitive data is replaced with non-sensitive data. In the payments industry, tokenization is used to protect the personal financial information of users by replacing it with a unique string of numbers.

Tokenization plays a critical role in fortifying online payments and safeguarding a user’s credit card information. Tokenization protects payment data in multiple ways, such as in the safekeeping of sensitive data and cryptographic control, ensuring that an unauthorized party cannot reveal the original PAN (Primary Account Number) associated with a generated token, and more.
In a tokenized transaction, the merchant never touches the customer’s actual payment details. Instead, when the customer pays the details are sent to the relevant provider’s Token Vault, and returned in the form of a unique “token” identifying the customer to the merchant. The next time the customer buys something from the merchant, the same token is used without the merchant having responsibility over the customer’s data.
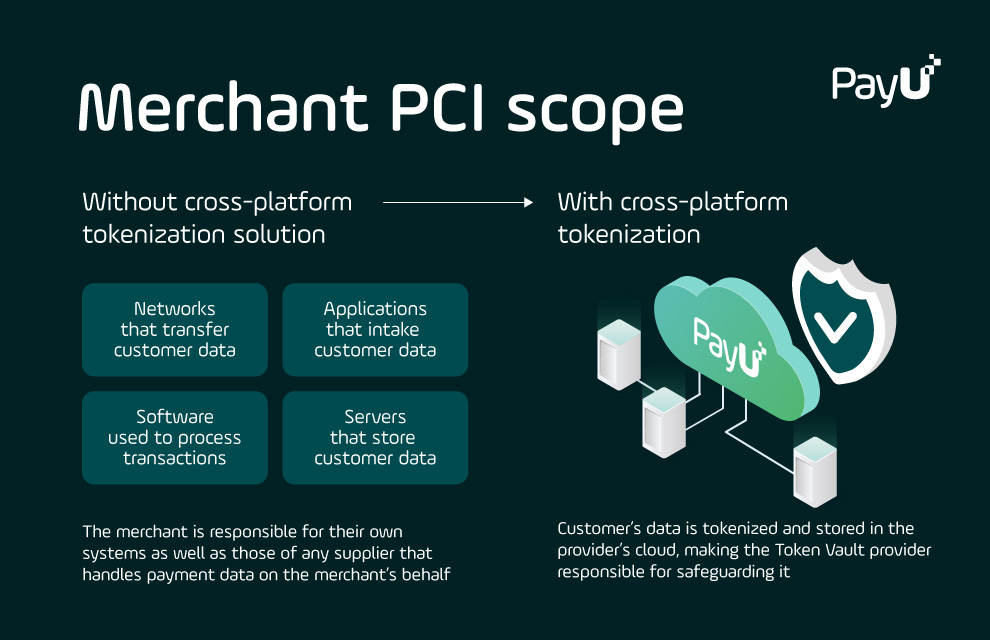
Many types of payment providers can operate a token vault, provided they meet the required level of PCI-DSS compliance. PayU is a PCI-DSS Level 1 Certified Processor, allowing us to offer merchants a single, cross-platform tokenization solution. Most PayU merchants use our tokenization technology to reduce PCI scope and risk.

PayU frees your business from needing to synchronize multiple token systems, consolidating them into one Token Vault, which contains all of your providers and payment methods. This helps to prevent provider lock-in when businesses wish to make changes to their payment stack and opt-out of specific providers.
Our tokenization technology references encrypted data stored on secure servers as a token, eliminating the burden of managing the storage of cardholder data and reducing the costs involved with PCI compliance.
Thanks to our PCI Level 1 certification, PayU is able to offer a streamlined and centralized Omni Token, allowing merchants to maintain a single card repository which can be used across payment providers without the need for oversight of sensitive customer data.
Tokenization solutions do not eliminate the need for merchants to maintain PCI-DSS compliance, but they can make compliance easier by lowering “PCI scope,” or the number of system components for which PCI-DSS regulations apply.
Through a collaboration with major credit card companies, PayU are also able to offer merchants the benefit of network tokens (on top of the tokenization process we already deploy). Network tokens are generated via tokenization services offered by the major card networks.
Although similar in concept to our existing tokenization, what differentiates network tokens is that they also allow payment processing without ever exposing the shopper’s actual card details. Network tokens offer higher approval rates in comparison with payments executed without network tokens, in addition to better security and an improved checkout experience.
From a compliance perspective, network tokens give merchants the opportunity to manage the network token’s status and suspend it if needed, and allow for easier adoption of EMVCo network token standards with minimal additional integration.
See how PayU supports PCI compliance while ensuring smooth and secure transactions.
Learn more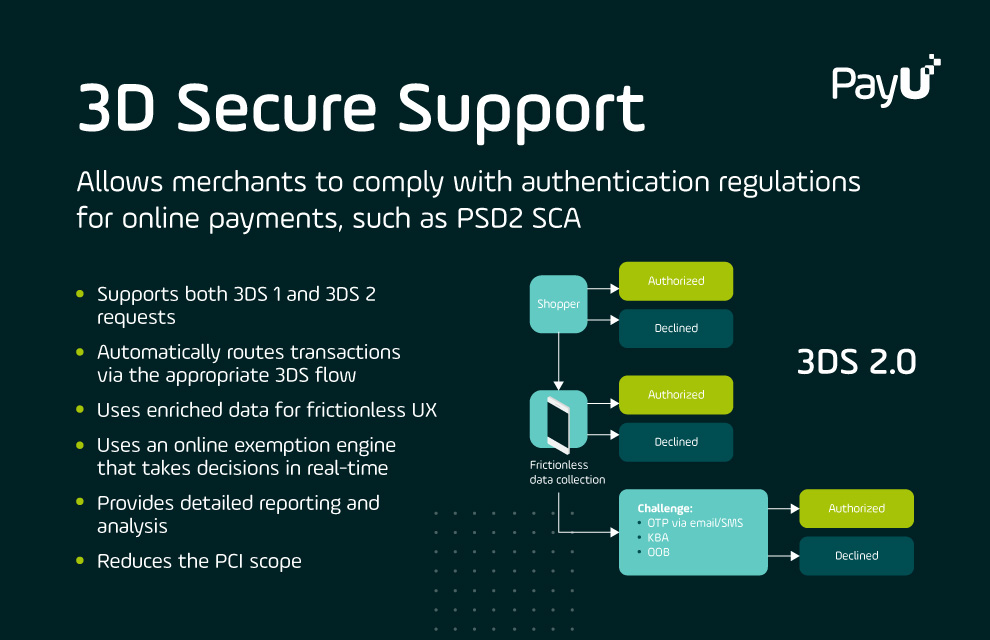
Learn about the 3DS 2 payment protocol and how PayU can help merchants manage the new guidelines.
Learn more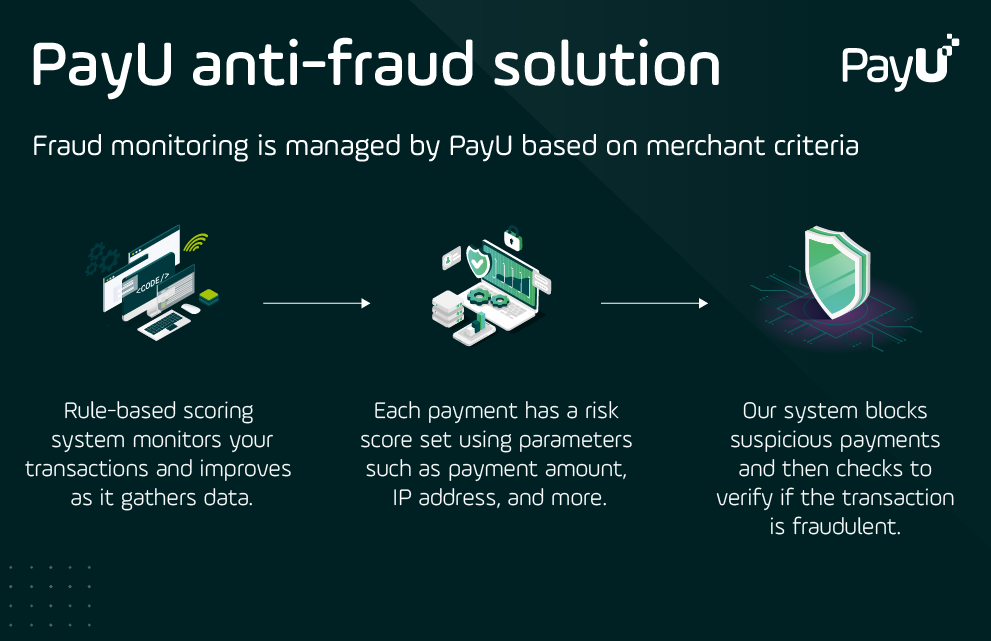
Discover PayU’s anti-fraud module and how it protects merchants as well as online shoppers.
Learn moreTokenization refers to the conversion of sensitive data into indecipherable “tokens” meant to protect and safeguard the original information.
Similar to data encryption and a byproduct of cryptography, tokenization of data in some cases is irreversible after the original information was tokenized. This makes the tokens completely safe in case of any data breach, because they are no longer readable.
Network tokenization is the process of converting payment card sensitive data into non-sensitive data represented by a token that can be used (or re-used in some cases) for payment transactions. The technology is provided by payment providers like PayU and card brands like Visa, Mastercard, American Express, etc.
Tokenization can have a variety of use cases depending on how they are used. Tokenization in online payments and e-commerce is used to secure sensitive card data and payment transactions for cards that are stored on file (in a system or platform). Tokens are generated for each transaction and are unique for each cardholder.
Card tokenization failure means that the system couldn’t tokenize the card information because the card expired, or (depending on the case) the system encountered an error. Since tokens are used for card-on-file transactions (both one-off and recurring payments), one common form of tokenization failure can occur when a customer has made an initial payment and in the meantime, the user’s card expired and their payment details were not updated.