22/07/2022
Stage 1: Checkout
Every successful e-commerce company knows the importance of ensuring that checkout is as seamless and convenient as possible for the end user. This helps merchants to reduce friction, cut down on cart abandonments, and drive more conversions.
One key aspect of optimizing the checkout process is providing the highest possible likelihood that customers can use their preferred payment method, by offering the right online payment method options for the target market audience.
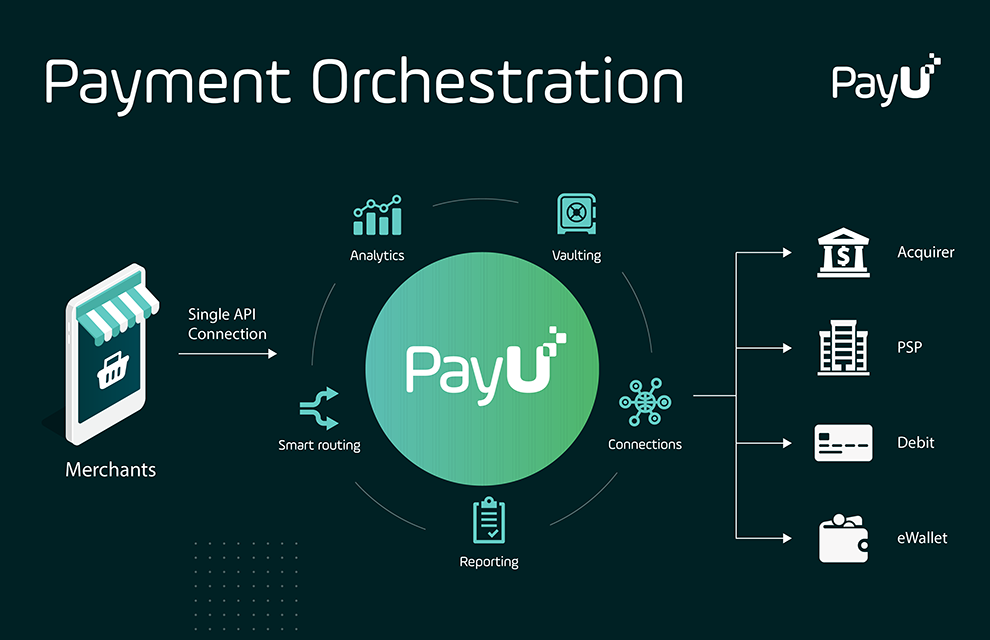
For cross-border merchants, payment methods are a particularly important part of e-commerce localization. To facilitate this, payment orchestration providers like PayU offer universal payment checkout options that allow merchants to offer the payment methods their customers want to use.
The presentation of available payment methods is based on rules set by the merchant. Merchants can offer different payment methods in different markets, depending on the local payment partners with whom the payment orchestration provider is integrated.
Orchestrating at this level requires having a global payment platform that can connect to multiple local payment providers; integrate with anti-fraud services for customer verification; and do it all through a payment gateway that provides an easy and high-quality checkout experience for the e-commerce customer.
Stage 2: Routing
After the customer enters their payment information is where the fun starts – and where payment orchestration really earns its stripes.
That’s because every online transaction must be routed through a maze of vendors and payment verification checkpoints before it can be completed successfully, and it’s in the routing phase where costs can really pile up. It’s also where payments have the highest chance of not going through.
Let’s think about it this way: every online transaction is sent through a payment gateway to a payment processor, who is responsible for routing it through all of the necessary steps to complete the payment. It’s up to the payment processor to determine how the payment will be routed.
But many payment processors are limited in terms of geography, the types of payment methods they can support, or the options they have for routing payments. As a result, merchants who are active in multiple markets might find themselves working with different payment processors for different markets. In addition to getting expensive, this can make it difficult to process payments efficiently. It can also lead to a lot of declined payments, should any links in any individual provider’s routing network fail.
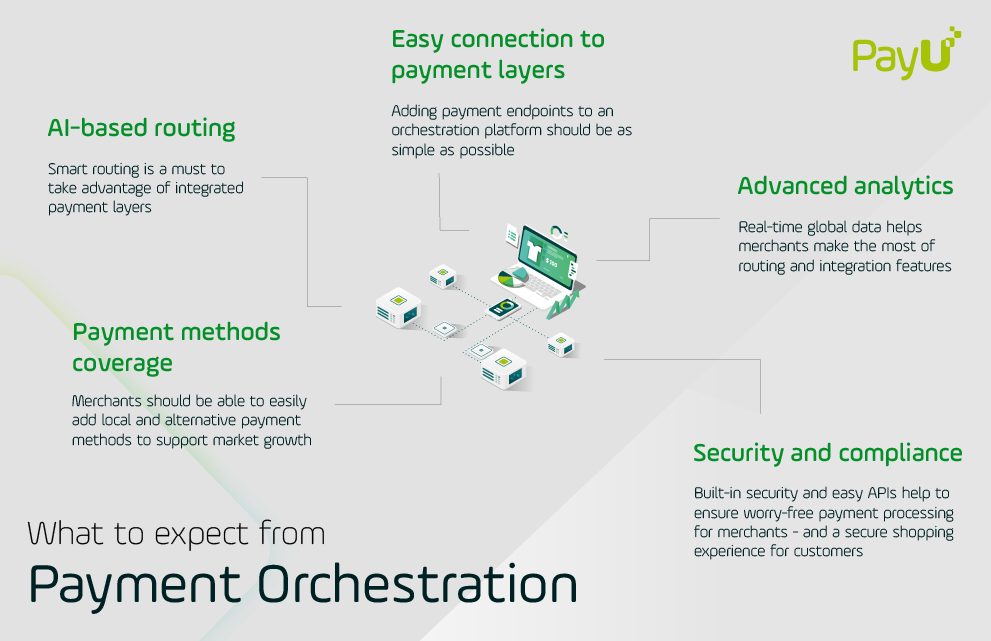
Payment orchestration is designed to address these common challenges by integrating multiple payment providers together into one global routing platform. Leveraging AI-based tools, payment orchestration helps businesses optimize routing traffic while saving payments that may otherwise have failed.
An orchestration platform, for example, can learn what the highest converting routing routes for certain types of payments and their respective merchants are, and then choose the optimal routing configuration based on this information.
Merchants can also set customized routing rules in order to optimize payment flows. Many businesses have hard or soft rules implemented by the routing engines they use. For example, if a merchant has multiple entities and provider relationships, they might decide to route certain currencies through a particular provider. To prevent failed payments, merchants can set up a retry policy to try declined payments through another provider.
Orchestrating at the routing level involves having multiple payment providers, as well as multiple merchant account relationships that work independently and without financial penalty. Smart routing technology is the engine that makes it all go, by optimizing payment traffic through the routing network based on merchant rules, machine learning, and more.
Stage 3: Settlement
A payment is completed when the funds end up in the merchant’s bank account. Prior to settlement, merchants naturally want the smallest amount possible skimmed off while maximizing sales and reducing chargebacks. This is where it’s essential to have a payment provider with an ideal merchant-friendly solution for settlements.
Transferring money across a number of currencies becomes less expensive if businesses can pay it out in the local currency and avoid the cost of currency conversion (FOREX). Then they can move the money back to their preferred base currency, at an exchange rate that works best.
At this level, payment orchestration focuses on making sure that the merchant can control how the money gets from the payment processor to their bank account – in the right currencies, at the correct rates.
 Payment Solutions
Payment Solutions Services
Services Products
Products Industries
Industries Resources
Resources About PayU
About PayU